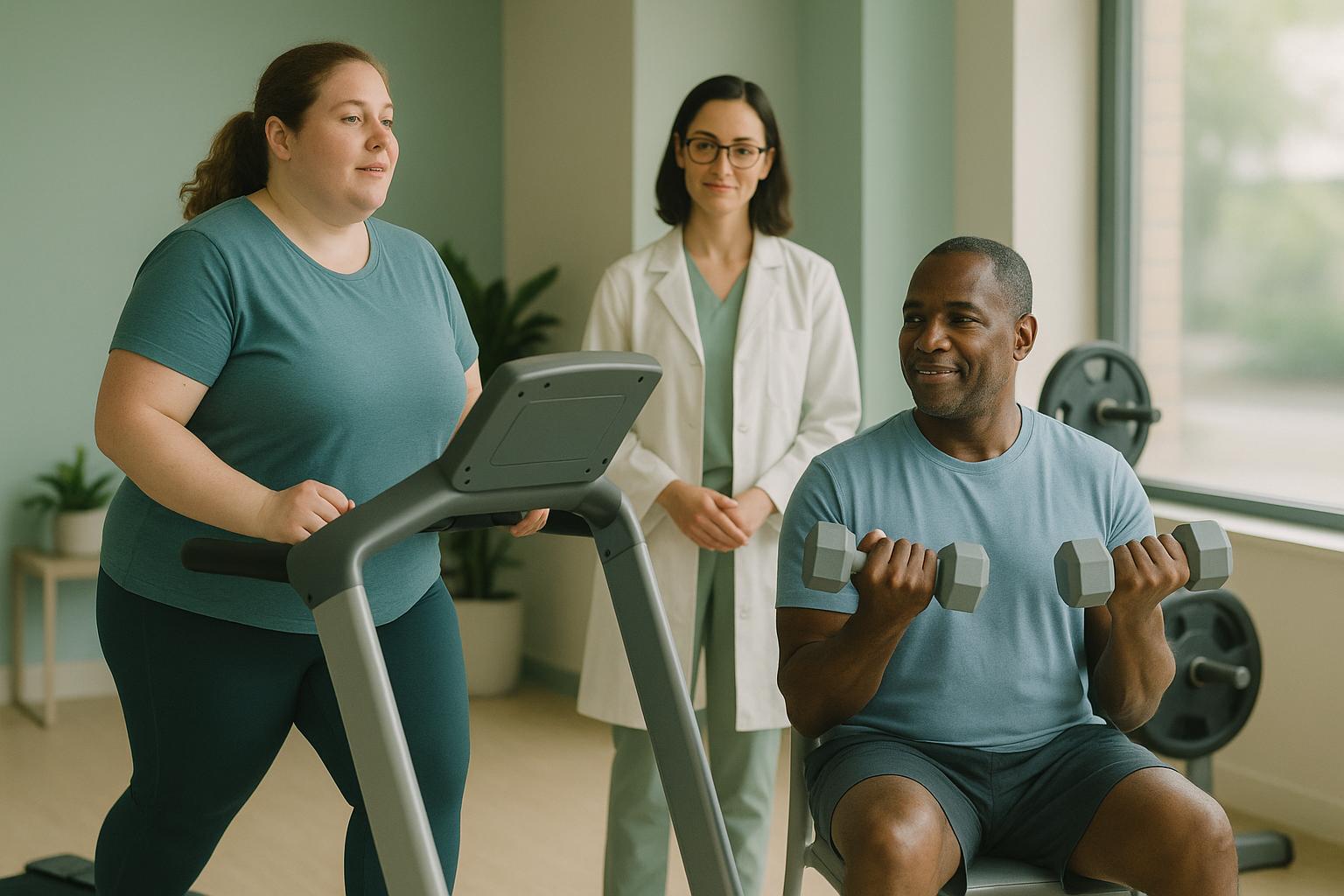
Cardio vs. Strength for GLP-1 Patients
Exercise is essential for GLP-1 patients to maintain health during weight loss. While GLP-1 medications like semaglutide and tirzepatide help reduce appetite and support weight loss, they don't protect against muscle loss or improve cardiovascular fitness. Without exercise, 25–40% of lost weight may come from lean muscle, which can slow metabolism and impact long-term health. Combining cardio and strength training can address these challenges.
- Cardio improves heart and lung health, boosts stamina, and aids fat loss.
- Strength training preserves muscle, supports metabolism, and prevents muscle loss.
A balanced plan includes at least 150 minutes of moderate cardio weekly and 2–3 strength training sessions to optimize results. Pairing exercise with adequate protein intake (1.2–2.0 g/kg body weight) further supports muscle maintenance. Always consult healthcare professionals to tailor a safe and effective fitness routine.
Cardio Training for GLP-1 Patients
What is Cardio Training?
Cardio training, often referred to as aerobic exercise, involves activities that elevate your heart rate and improve stamina by engaging large muscle groups. Examples include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging. These exercises are suitable for a wide range of fitness levels and can be modified in intensity, making them an excellent choice for GLP-1 patients who are starting an exercise routine or managing medication side effects. Starting small - like a 10-minute walk - and gradually increasing duration and intensity allows your body to adjust over time. This gradual approach makes cardio an effective way to complement your medical treatment while easing into physical activity.
Cardio Benefits for GLP-1 Patients
Incorporating cardio training into your routine offers multiple benefits that align well with GLP-1 treatments. Aerobic exercise helps burn calories and supports fat loss, complementing the appetite-regulating effects of GLP-1 medications. Beyond weight management, cardio strengthens the heart, improves lung function, and enhances oxygen delivery - areas that medication alone cannot address. It also boosts energy levels and uplifts mood by releasing endorphins, which can be particularly helpful during the weight-loss process. Even light to moderate activity, such as 30 minutes of walking most days of the week, can significantly improve overall health.
Cardio Challenges for GLP-1 Users
While cardio has numerous advantages, it may pose specific challenges for individuals taking GLP-1 medications. Side effects like nausea, fatigue, or reduced appetite can make it harder to sustain longer or more intense workouts. Some patients may also notice an increase in hunger after cardio sessions, which could lead to overeating and reduce the calorie deficit needed for weight loss. Additionally, cardio alone may not be enough to preserve muscle mass, meaning some weight loss could come from lean muscle rather than fat. Opting for low-impact cardio and gradually increasing intensity can help address these challenges while maximizing the benefits of your exercise routine.
The Ozempic Workout Plan No One’s Telling You About
Strength Training for GLP-1 Patients
While cardio is excellent for improving heart health and endurance, strength training plays a different role by focusing on muscle preservation and supporting your metabolism.
What is Strength Training?
Strength training involves using resistance - whether through weights, resistance bands, or your own body weight - to build and maintain muscle. Examples include exercises like weightlifting, squats, push-ups, and planks. Unlike cardio, which primarily raises your heart rate, strength training emphasizes controlled movements and gradually increasing resistance to target muscle growth and retention.
For individuals on GLP-1 medications, this type of exercise is especially important. These medications can lead to rapid weight loss, which may include the loss of muscle mass. Strength training helps signal your body to hold onto and even build muscle tissue, even when your calorie intake is reduced due to the appetite-suppressing effects of the medication.